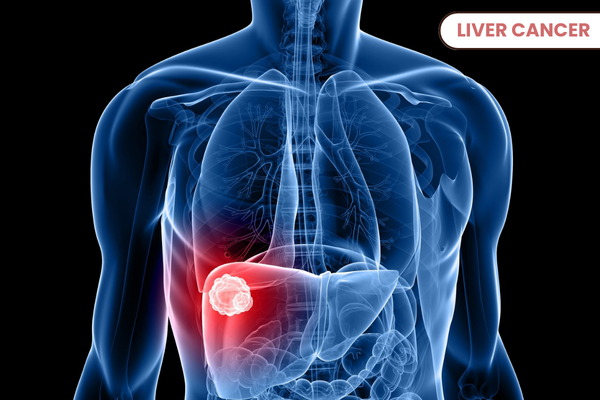
Liver Cancer:
Liver cancer is a serious condition that starts in the liver, an important organ located on the right side of your abdomen. It plays a crucial role in digesting food and filtering toxins from the body. When cells in the liver grow uncontrollably, they can form a tumor, which can lead to liver cancer. The disease can be primary, meaning it begins in the liver, or secondary, meaning it spreads from another part of the body.
What Causes Liver Cancer?
There are several factors that increase the risk of liver cancer, including:
- Chronic Liver Disease: Conditions like hepatitis B or C, cirrhosis (scarring of the liver), and fatty liver disease can damage liver cells and increase the risk of cancer.
- Alcohol Consumption: Drinking large amounts of alcohol over time can cause liver damage, which can eventually lead to liver cancer.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can contribute to fatty liver disease, which in turn increases the risk of liver cancer.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes, especially those with poor blood sugar control, are at a higher risk.
- Family History: A family history of liver cancer can make you more likely to develop the disease.
While these are common risk factors, not everyone with these conditions will develop liver cancer, and some people without these risk factors can still get it.
Symptoms of Liver Cancer
In the early stages, liver cancer often doesn't cause any noticeable symptoms. However, as the disease progresses, you may experience:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Feeling full after eating only a small amount of food
- Abdominal pain or discomfort, especially on the right side
- Swelling or fluid buildup in the abdomen
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes)
- Fatigue or weakness
- Nausea and vomiting
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosis of Liver Cancer
If your doctor suspects liver cancer, they will perform a variety of tests, including:
- Blood Tests: These can detect liver function and markers that may indicate liver cancer.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, CT scans, or MRIs can help doctors see any tumors in the liver.
- Liver Biopsy: A small tissue sample may be taken from the liver to confirm if cancer cells are present.
Treatment Options
The treatment for liver cancer depends on the stage of the cancer, your overall health, and how well your liver is functioning. Common treatments include:
- Surgery: If the tumor is small and confined to one area, surgery may be done to remove part of the liver or the entire liver.
- Liver Transplantation: For people with advanced liver cancer and severe liver disease, a liver transplant might be an option.
- Ablation Therapy: This involves using heat or cold to destroy the tumor.
- Radiation Therapy: High-energy rays are used to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors.
- Chemotherapy: This treatment uses drugs to kill or stop the growth of cancer cells, often used in advanced stages.
- Targeted Therapy: This treatment focuses on targeting specific molecules involved in cancer growth.
- Immunotherapy: This boosts the body’s immune system to help fight cancer cells.
Prevention
While liver cancer cannot always be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk, such as:
- Getting vaccinated against hepatitis B
- Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Managing chronic conditions like diabetes and fatty liver disease
Liver cancer is a serious disease, but early detection and treatment can greatly improve outcomes. If you have risk factors or experience symptoms, speak with a doctor for advice and possible screenings.
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *




.png)