Uterine Cancer:
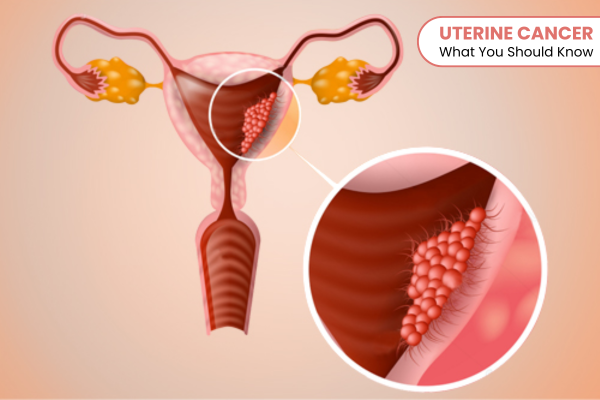
Uterine cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the uterus, the pear-shaped organ in a woman’s pelvis where a baby grows during pregnancy. It is one of the most common cancers of the female reproductive system. The most common type of uterine cancer is called endometrial cancer, which begins in the lining of the uterus (endometrium). Another, less common type is uterine sarcoma, which starts in the muscle or other tissue of the uterus.
What Causes Uterine Cancer?
The exact cause of uterine cancer is not fully known, but certain factors can increase your risk. These include:
- Hormonal imbalance, especially too much estrogen
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Early menstruation or late menopause
- Never being pregnant
- Family history of uterine or colon cancer
- Certain genetic conditions, like Lynch syndrome
It’s important to remember that having one or more of these risk factors doesn’t mean you will get uterine cancer, but it may increase your chances.
Common Symptoms
Uterine cancer often shows early warning signs. The most common symptom is:
- Unusual vaginal bleeding, especially after menopause
Other symptoms may include:
- Bleeding between periods
- A watery or blood-tinged discharge
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Pain during sex or urination
If you experience any of these symptoms, especially postmenopausal bleeding, you should consult your doctor right away.
Diagnosis
If uterine cancer is suspected, your doctor may recommend:
- Pelvic examination
- Ultrasound to view the uterus
- Endometrial biopsy, where a small sample of tissue is taken from the uterus and tested
- Hysteroscopy, a procedure to look inside the uterus using a thin tube with a camera
- Imaging tests like CT scans or MRIs to check if the cancer has spread
Early diagnosis is key to successful treatment.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the stage and type of cancer. Common treatment options include:
- Surgery – The most common treatment is removing the uterus (hysterectomy), often along with the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
- Radiation therapy – High-energy rays are used to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy – Anti-cancer drugs are used to destroy cancer cells throughout the body.
- Hormone therapy – Used in some cases to block hormones that help the cancer grow.
- Targeted therapy or immunotherapy—advanced treatments for certain types of uterine cancer.
Your doctor will guide you through the best treatment plan based on your case.
Prevention & Care
While not all cases can be prevented, some steps may reduce your risk:
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Exercise regularly
- Manage health conditions like diabetes
- Use birth control pills with doctor’s guidance (they may lower risk)
- Regular check-ups, especially after menopause
Final Words:
Uterine cancer is treatable, especially when detected early. Pay attention to your body, know the warning signs, and don’t ignore unusual bleeding. If you have any concerns, talk to your doctor. Early care can save lives.
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *




.png)